Environment Variables Management
Overview
Environment variables are key-value pairs used to configure your application’s behavior without hardcoding values in your source code. Haddock provides a comprehensive interface to manage these variables directly from your project settings, including support for secret variables that protect sensitive information.
Accessing Environment Variables
- Navigate to your project’s details page
- Click on the “Settings” tab
- Click to expand the accordion and reveal the environment variables interface
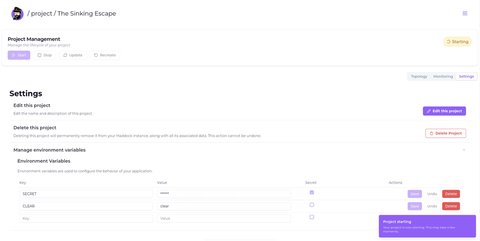
Environment Variables Interface
The environment variables management interface displays a table with the following columns:
- Key: The environment variable name
- Value: The variable value (masked for secret variables)
- Secret: Checkbox indicating if the variable is secret
- Actions: Save, Undo, and Delete buttons for each variable
Managing Environment Variables
Adding New Variables
To add a new environment variable:
- Scroll to the bottom of the environment variables section
- Fill in the Key field with your variable name
- Enter the Value for your variable
- Optional: Check the Secret checkbox if the variable contains sensitive information
- Click the “Add” button to create the variable
Variable Naming
Use uppercase letters with underscores for environment variable names (e.g., DATABASE_URL, API_KEY) following common conventions.
Editing Existing Variables
Non-Secret Variables
For regular (non-secret) variables:
- Locate the variable in the list
- Modify the Key or Value directly in the table
- Click the “Save” button to apply changes
- Use “Undo” to revert unsaved changes
Secret Variables
For secret variables:
- The Value field will display masked characters (••••••)
- You can still update the Key and Value, but the value remains hidden
- Click “Save” to apply changes
- The updated value will not be visible for security reasons
Converting Variables to Secret
You can convert a regular variable to a secret variable:
- Locate the non-secret variable
- Check the Secret checkbox
- Click “Save” to apply the change
- The variable value will now be masked
One-Way Conversion
Important: Once a variable is marked as secret, you cannot convert it back to a non-secret variable. This is a security feature to prevent accidental exposure of sensitive data.
Deleting Variables
To remove an environment variable:
- Locate the variable you want to delete
- Click the “Delete” button (red button) in the Actions column
- The variable will be removed immediately
- A confirmation notification will appear in the bottom right corner
Secret Variables
What Are Secret Variables?
Secret variables are environment variables that contain sensitive information such as:
- API keys and tokens
- Database passwords
- Encryption keys
- OAuth secrets
- Third-party service credentials
Secret Variable Behavior
When a variable is marked as secret:
- Hidden Values: The value is masked with dots (••••••) in the interface
- Edit Capability: You can still edit the key and update the value
- One-Way Protection: Cannot be converted back to non-secret
- Runtime Access: Still accessible to your application at runtime
- Security: Protected from accidental exposure in logs or interface
Best Practices
Security Considerations
Use Secret Variables For:
- Database connection strings
- API keys and authentication tokens
- Encryption keys
- OAuth client secrets
- Any sensitive configuration data
Avoid Secrets In Code:
- Never hardcode sensitive values in your source code
- Use environment variables for all configuration
- Mark sensitive variables as secret immediately
Organization Tips
Naming Conventions:
- Use descriptive, uppercase names:
DATABASE_URL,SMTP_PASSWORD - Group related variables with prefixes:
AWS_ACCESS_KEY,AWS_SECRET_KEY - Be consistent across projects and environments
Documentation:
- Document the purpose of each variable
- Note which variables are required vs. optional
- Maintain a separate record of secret variable purposes
Development Workflow
- Add Variables: Create variables in the Haddock interface
- Test Changes: Restart your project to test new configurations
- Validate: Ensure your application correctly reads the variables
- Document: Keep track of variable purposes and dependencies
Troubleshooting
Common Issues
Variables Not Available in Application:
- Ensure you’ve restarted the project after making changes
- Check that variable names match exactly (case-sensitive)
- Verify your application is reading from the correct environment
Secret Variables Not Working:
- Secret variables are accessible to your application even though hidden in the UI
- Check your application’s environment variable reading logic
- Ensure the variable name hasn’t changed during editing
Changes Not Persisting:
- Make sure to click “Save” after editing variables
- Don’t forget to restart the project for changes to take effect
- Check for any error notifications in the bottom right corner
Validation Tips
- Test your application with different variable values
- Use non-secret variables during development and convert to secret for production
- Regularly review and clean up unused environment variables
- Monitor application logs for environment-related errors
Testing Environment Variables
Create a simple endpoint or script in your application that displays environment variable names (not values) to verify they’re properly loaded.